Ecosystem Targets and Supporting Indicators
Extent of Hypoxia
Target: Measurably reduce the area of hypoxia in Long Island Sound from pre-2000 Dissolved Oxygen TMDL averages to increase attainment of water quality standards for dissolved oxygen by 2035, as measured by the five-year running average size of the zone.
View Implementation Actions for Extent of HypoxiaProgress
| Area in Square Miles | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Area of Hypoxia (sq. mi.) | Five-year Running Average (sq. mi.) | Percent to Goal |
| baseline* | 208 | ||
| 1987 | 309 | ||
| 1988 | 251 | ||
| 1989 | 328 | ||
| 1990 | 174 | ||
| 1991 | 122 | 237 | 63 |
| 1992 | 80 | 191 | 79 |
| 1993 | 202 | 181 | 83 |
| 1994 | 393 | 194 | 77 |
| 1995 | 305 | 220 | 68 |
| 1996 | 220 | 240 | 63 |
| 1997 | 30 | 230 | 65 |
| 1998 | 168 | 223 | 67 |
| 1999 | 121 | 169 | 89 |
| 2000 | 173 | 142 | 106 |
| 2001 | 133 | 125 | 120 |
| 2002 | 130 | 145 | 103 |
| 2003 | 345 | 180 | 83 |
| 2004 | 202 | 197 | 76 |
| 2005 | 177 | 197 | 76 |
| 2006 | 199 | 211 | 71 |
| 2007 | 162 | 217 | 69 |
| 2008 | 180 | 184 | 82 |
| 2009 | 169 | 177 | 85 |
| 2010 | 101 | 162 | 93 |
| 2011 | 130 | 148 | 101 |
| 2012 | 288 | 174 | 86 |
| 2013 | 80 | 154 | 97 |
| 2014 | 87 | 137 | 109 |
| 2015 | 38 | 125 | 120 |
| 2016 | 197 | 138 | 109 |
| 2017 | 70 | 95 | 158 |
| 2018 | 52 | 89 | 169 |
| 2019 | 89 | 89 | 169 |
| 2020 | 63 | 94 | 160 |
| 2021 | 142 | 83 | 181 |
| 2022 | 87 | 87 | 170 |
| 2023 | 127 | 102 | 145 |
| 2024 | 43 | 92 | 163 |
| *baseline is avg. of hypoxia from beginning of wq monitoring program to TMDL agreement (1987-2000). | |||
Status and Trends
Meeting the hypoxia reduction ecosystem target by increasing oxygen concentrations in the bottom waters is ahead of schedule. The target is measured as the five-year rolling average of the bottom water area with < 3 mg/L dissolved oxygen. The five-year rolling average for 2019-2023 was 102 square miles of hypoxia compared to an average of 208 square miles from the 1987-1999 baseline, a 51 percent reduction. Based on the 2015 CCMP, a 28 percent reduction from the baseline (to about 150 square miles) is necessary to achieve a measurable reduction (see data note). While achieving a measurable reduction in hypoxia from 2019-2023 is a major achievement, further reductions in the hypoxic area are needed through 2035 in order to fully attain water quality standards and achieve the ecosystem target goal.
The five-year average hypoxic area increased slightly by 15 square miles from last year’s five-year average of 87 square miles (for 2019-2023) the maximum area of hypoxia increased – from 87 square miles in 2022 to 127 square miles in 2023. Dry summer conditions during summer 2022 likely reduced nutrient loading to the Sound from the watershed, likely contributing to the observed reduction in hypoxic area. Excess nutrient loading contributes to conditions that result in hypoxic, or oxygen-depleted, waters.
In assessing trends, LISS uses the five-year rolling average, instead of from year to year, because conditions in any given year could be impacted by variable factors, such as extreme changes in heat or precipitation, which average out over time.
The years 1987-1999 are used as a benchmark (or the baseline) because they represent the beginning of Long Island Sound Study’s water quality monitoring program, prior to the Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) agreement in 2000 to reduce nitrogen loads into the Sound.
Challenges
Warming water temperatures will reduce the amount of oxygen that the water can contain, making it more difficult to meet the target long term. In addition to weather variables affecting the area of hypoxia year to year, longer-term climate influences will affect the vulnerability of the Sound to hypoxia. Improvements in monitoring, including increased monitoring in embayments, will better define areas affected by hypoxia, and the factors contributing to it.
How is This Target Measured?
Routine monitoring of bottom-water hypoxia is done monthly throughout the year and biweekly in the summer by the Connecticut Department of Energy and Environmental Protection (CT DEEP).
Additional year-round monitoring is conducted by the Interstate Environmental Commission in Western Long Island Sound and the Narrows. The Long Island Sound Integrated Coastal Observing System (LISICOS) also deploys real-time monitoring instruments on buoys across the Sound, including three with bottom water oxygen sensors in the Western Sound. The three monitoring programs help provide a comprehensive long-term data set on both the area and duration of hypoxia, with the monitoring data going back to 1987 (initially conducted by the University of Connecticut from 1987-1990, and beginning with CT DEEP since 1991).
Bottom hypoxia is measured by lowering instruments with multiple sensors (including dissolved oxygen) through the water column from a research vessel or smaller boat.
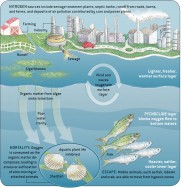
Importance
Hypoxia, a deficiency in the amount of oxygen in the water, can be harmful or lethal to fish, invertebrates, and other animals and therefore decrease or eliminate them from Long Island Sound.
Hypoxia may also limit the growth of animals that are exposed but not killed.
Contact
Dr. James Ammerman, Long Island Sound Study james.ammerman@longislandsoundstudy.net
Source of Data
CT DEEP (primary data source), also the Interstate Environmental Commission for Western Long Island Sound, and LISICOS.
DATA NOTES
- The technical explanation on how the target was selected is found in Appendix B of the Comprehensive Conservation and Management Plan.
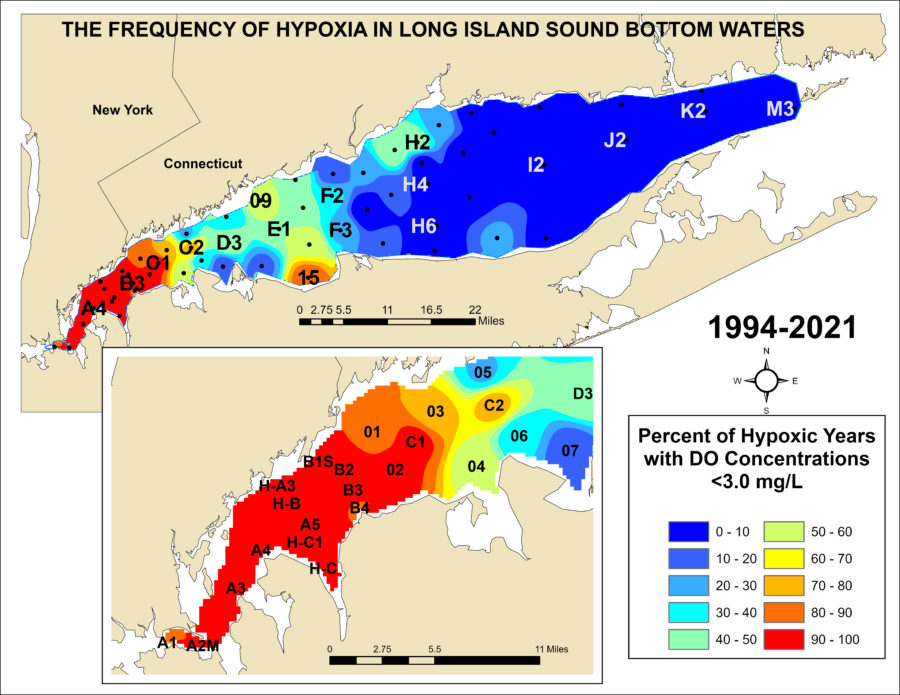 Hypoxia is more
Hypoxia is more